Global Trends in Co-Living and Co-Working Spaces in 2026
A New Geography of Work and Home
By 2026, co-living and co-working have moved from experimental niches to a central feature of how people in major cities and emerging hubs around the world organize their lives, careers, and communities. What began as a response to soaring urban housing costs and the early waves of digital nomadism has matured into a complex ecosystem of specialized operators, institutional investors, municipal regulators, and a new generation of residents and professionals who increasingly expect flexibility, community, and purpose from both their homes and their workplaces. For WorldsDoor.com, whose readers span health, travel, culture, lifestyle, business, technology, environment, and society, the evolution of co-living and co-working offers a powerful lens through which to understand broader shifts in how people live, work, and connect across continents.
In cities from New York and London to Berlin, Singapore, São Paulo, Cape Town, and Bangkok, the blending of residential and professional environments has created new opportunities and new risks. The rise of hybrid work models, the normalization of remote collaboration tools, and the global mobility of skilled workers have converged to reshape real estate, labor markets, and social norms. At the same time, concerns around mental health, sustainability, urban inequality, and cultural displacement are forcing governments, companies, and communities to reconsider what "shared space" should mean in the mid-2020s and beyond. Against this backdrop, co-living and co-working are no longer simply about desk rentals or shared kitchens; they are becoming platforms for reimagining health, education, community, and even governance.
From Emergency Experiment to Mature Asset Class
The pandemic era accelerated remote work adoption and pushed many organizations to embrace flexible office arrangements. By 2026, this shift has solidified into a durable structural change. Research from institutions such as OECD and World Economic Forum has documented the long-term impact of hybrid and remote work on productivity, skills, and urban form, while major enterprises in the United States, United Kingdom, Germany, Canada, Australia, and across Asia now maintain distributed workforces as a matter of strategy rather than contingency.
Co-working operators that survived the volatility of the early 2020s have restructured their business models, focusing on longer-term corporate contracts, curated communities, and data-driven space utilization. At the same time, institutional investors, guided by analyses from organizations such as CBRE and JLL, increasingly classify flexible workspaces and co-living developments as distinct asset classes within commercial real estate portfolios. In global hubs from London and Amsterdam to Singapore and Seoul, mixed-use developments now routinely integrate flexible office floors, co-living units, and public or semi-public community spaces.
For readers of WorldsDoor.com interested in the intersection of business and lifestyle, this financial maturation is critical. Co-living and co-working are no longer marginal lifestyle experiments; they are backed by pension funds, sovereign wealth funds, and large real estate investment trusts. This influx of capital has facilitated higher design standards, better digital infrastructure, and more robust amenities, but it has also raised questions around affordability, gentrification, and the homogenization of local culture, which are central to ongoing discussions on global business and society.
The Hybrid Work Culture Behind Co-Working's Resilience
The persistence of hybrid work is the single most important driver of co-working's global resilience. Survey data from organizations such as Gallup and McKinsey & Company indicate that knowledge workers in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia now expect a mix of remote and in-office days as a baseline condition of employment. Large employers in the United States, United Kingdom, Germany, and Japan increasingly offer "work from anywhere" arrangements within certain time zones, and this flexibility has catalyzed demand for well-equipped, community-oriented work hubs in secondary and even tertiary cities.
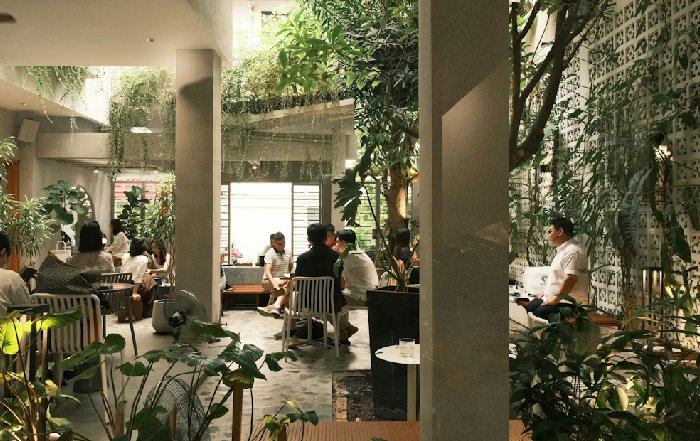
In response, co-working providers have evolved beyond the early open-plan model. They now prioritize acoustic privacy, ergonomic design, and health-supportive features such as natural light, air filtration, and access to green spaces, aligning with best practices promoted by organizations like WELL Building Standard. These environments are not just about productivity but also about wellbeing, which connects directly to WorldsDoor.com's ongoing coverage of health and lifestyle, particularly mental health and burnout in high-pressure industries.
Hybrid workers increasingly use co-working memberships as a way to separate home and work without returning to the rigidity of traditional offices. In cities such as Toronto, Melbourne, Stockholm, and Singapore, suburban and neighborhood-scale co-working hubs have become common, reducing commute times while preserving professional social interaction. This distributed network model supports local businesses, contributes to more balanced urban traffic patterns, and allows parents and caregivers more flexible daily rhythms, which in turn influences broader societal norms around work-life integration.
Co-Living as a Response to Housing, Loneliness, and Mobility
Parallel to the evolution of co-working, co-living has emerged as a multifaceted response to housing affordability, urban loneliness, and the rising mobility of younger and mid-career professionals. In major cities across Europe, North America, and Asia, high rents and limited supply have made traditional apartments less accessible, especially for people at early career stages or those relocating internationally. Co-living operators in cities such as London, Berlin, New York, San Francisco, Singapore, and Tokyo offer furnished rooms, communal kitchens, shared lounges, and community programming, bundling utilities, cleaning, and digital infrastructure into a single monthly fee.
While early co-living brands targeted mostly young professionals, the segment has diversified. In 2026, there are co-living spaces designed specifically for remote workers, creatives, graduate students, single parents, active seniors, and even intergenerational communities. The emphasis on shared experiences and curated events is partly a response to the growing recognition of loneliness as a public health issue, highlighted by organizations such as the World Health Organization and health ministries in countries including the United States, United Kingdom, and Japan. For many residents, co-living offers not only cost efficiencies but also a sense of belonging and mutual support that traditional rental arrangements often lack.
For globally mobile professionals, particularly those in technology, design, and entrepreneurship, co-living has become an enabling infrastructure for multi-city lifestyles. Remote workers may spend several months in Barcelona, then relocate to Lisbon, Singapore, or Chiang Mai, relying on co-living networks for consistent standards of comfort, connectivity, and community. This phenomenon intersects directly with WorldsDoor.com's focus on travel and lifestyle, as digital nomadism evolves from a fringe subculture into a mainstream option for skilled workers in Europe, Asia, and the Americas.
Regional Patterns: North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific
Despite global commonalities, co-living and co-working trends manifest differently across regions. In North America, particularly in the United States and Canada, co-working has become deeply integrated into the startup ecosystem and the corporate real estate strategies of large firms. Major cities such as New York, San Francisco, Toronto, and Vancouver host dense networks of flexible workspaces, while smaller cities in the Midwest and Atlantic Canada have embraced co-working as a tool for revitalizing downtown cores. Co-living in North America often takes the form of large, amenity-rich complexes, appealing to young professionals who value convenience, networking, and access to urban culture.
In Europe, co-living and co-working are closely linked to broader debates about housing policy, urban sustainability, and social inclusion. Cities such as Berlin, Amsterdam, Copenhagen, and Barcelona have experimented with cooperative housing models and municipally supported co-working hubs, sometimes in partnership with universities and cultural institutions. Organizations like Eurostat and European Environment Agency have tracked how shared spaces intersect with climate goals, urban density, and transport planning, influencing local regulations that either encourage or constrain new developments. For WorldsDoor.com readers interested in European culture and society, these experiments offer insight into how values of social democracy, environmental stewardship, and cultural preservation shape built environments.
Across Asia-Pacific, from Singapore and Hong Kong to Seoul, Tokyo, Bangkok, and Sydney, co-living and co-working are often framed as solutions to extreme land scarcity, long commutes, and intense work cultures. In Singapore, for instance, government agencies and private developers collaborate on integrated developments that combine housing, offices, and leisure facilities, supported by advanced digital infrastructure and transit connectivity. In South Korea and Japan, micro-apartments and capsule co-living concepts coexist with more spacious, community-oriented projects, reflecting diverse consumer preferences and demographic pressures. Reports from organizations such as Asian Development Bank and UN-Habitat highlight how these models are influencing urban planning across rapidly growing cities in Southeast Asia and beyond.
Health, Wellbeing, and the Human Side of Shared Spaces
Health considerations have moved to the center of co-living and co-working design. Beyond basic sanitation and ventilation, operators now emphasize mental health, social connection, and work-life balance as core value propositions. Spaces increasingly incorporate quiet rooms, meditation areas, fitness facilities, and access to nature, aligning with evidence from institutions such as Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health regarding the relationship between built environments and cognitive performance, stress, and overall wellbeing.
For WorldsDoor.com, which regularly explores health, lifestyle, and environment, this convergence is significant. Co-working spaces that offer ergonomic furniture, natural materials, biophilic design elements, and healthy food options are not only differentiating themselves in competitive markets but also contributing to broader public health outcomes. Co-living communities that prioritize quiet hours, inclusive social events, and conflict resolution protocols help reduce isolation and interpersonal stress, particularly for residents living far from family support networks in countries such as Germany, Australia, France, and Brazil.
At the same time, the psychological demands of constant social proximity should not be underestimated. Shared kitchens, lounges, and work areas can become sources of friction if expectations are poorly managed or if community norms are not clearly articulated. Some operators have responded by employing community managers trained in facilitation and conflict mediation, drawing on best practices from social psychology and organizational behavior. Others partner with digital health platforms and local providers, encouraging residents and members to access counseling or coaching services when needed. This integration of health and shared living underscores the importance of trust and professionalism in the sector, reinforcing the need for transparent governance and ethical standards.
Technology as the Invisible Infrastructure of Shared Life
The digital backbone of co-living and co-working has become more sophisticated, integrating access control, booking systems, community platforms, and data analytics. Cloud-based tools, high-bandwidth connectivity, and secure collaboration platforms, many of them popularized by companies whose practices are profiled by organizations like Gartner, enable seamless work across time zones and geographies. Members expect frictionless check-in, room booking, and payment experiences, while operators rely on data to optimize space utilization, energy consumption, and service offerings.
For remote workers and distributed teams, secure connectivity and privacy protections are paramount. The handling of personal and behavioral data by co-working and co-living operators raises questions about surveillance, consent, and data governance. Regulatory frameworks such as the EU's General Data Protection Regulation, tracked by resources like European Commission's digital policy portal, have set high standards for data protection, influencing global practices. In Asia and North America, evolving privacy laws are pushing operators to adopt stronger encryption, transparent privacy policies, and user control over data.
Technology also plays a key role in community building. Many co-living and co-working networks maintain internal social platforms where members can share projects, organize events, or exchange services. These digital spaces extend the physical community, enabling cross-location collaboration and mentorship, particularly valuable for entrepreneurs and freelancers in sectors such as software development, design, and creative industries. For readers following WorldsDoor.com's coverage of technology and innovation, the co-living and co-working ecosystem offers a living laboratory for how digital tools mediate human relationships in high-density, high-mobility environments.
Sustainability and the Ethics of Shared Urban Futures
Sustainability is no longer a peripheral marketing claim; in 2026 it is central to how leading co-living and co-working operators design, build, and manage their spaces. Shared infrastructure can, in principle, reduce per-capita energy use, water consumption, and material waste, aligning with climate goals articulated by organizations such as the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change and UN Environment Programme. High-efficiency building systems, renewable energy integration, and circular economy initiatives, such as furniture reuse and community repair workshops, are increasingly common in new developments.
However, the environmental benefits of co-living and co-working depend heavily on implementation details. A co-living complex that encourages frequent international travel among residents may inadvertently increase overall carbon footprints, even if the building itself is energy efficient. Similarly, co-working spaces that operate 24/7 with low occupancy during off-peak hours may waste energy despite modern systems. These tensions highlight the importance of rigorous sustainability metrics and transparent reporting, which can be informed by frameworks promoted by organizations such as Global Reporting Initiative.
Ethical considerations extend beyond environmental impacts to encompass labor practices, community relations, and cultural integrity. The arrival of upscale co-living and co-working hubs in historically low-income neighborhoods in cities such as San Francisco, Berlin, Cape Town, and Rio de Janeiro can accelerate gentrification, displace long-term residents, and alter local cultural dynamics. Operators that position themselves as community builders must therefore engage with local stakeholders, support inclusive hiring, and contribute to neighborhood development in ways that respect existing social fabrics. For WorldsDoor.com, whose readers are deeply engaged with sustainability and ethics, this intersection of environmental responsibility and social justice is a critical dimension of the co-living and co-working story.
Education, Entrepreneurship, and the Future of Talent
Co-living and co-working spaces are increasingly intertwined with education and entrepreneurship. Universities and business schools in the United States, United Kingdom, Germany, France, Singapore, and Australia are partnering with flexible workspace providers to offer students and alumni access to innovation hubs that blend classrooms, labs, and co-working environments. This trend reflects a broader shift toward lifelong learning and project-based education, as documented by organizations such as UNESCO, which emphasize the need for adaptive skills in rapidly changing labor markets.
Startup accelerators and incubators now frequently operate out of co-working spaces, leveraging shared infrastructure and community networks to support founders. In some cases, co-living is integrated directly into these programs, enabling entrepreneurs to live and work alongside peers during intensive development periods. This model has gained traction in cities such as London, Berlin, Tel Aviv, Singapore, and San Francisco, where access to networks and serendipitous encounters can be as valuable as formal mentorship. For WorldsDoor.com readers tracking innovation, education, and business, these hybrid environments illustrate how physical space can accelerate knowledge transfer, collaboration, and venture creation.
The implications for talent mobility are profound. Young professionals from South Africa, Brazil, India, and Southeast Asia can now participate in global startup ecosystems without relocating permanently, using co-living and co-working networks as stepping stones for short-term residencies in innovation hubs. Conversely, professionals from North America and Europe can immerse themselves in emerging markets, gaining local insights while contributing expertise. This bidirectional flow supports more diverse and inclusive innovation landscapes, although it also raises questions about brain drain, cultural appropriation, and the equitable distribution of economic benefits.
Cultural Diversity, Inclusion, and Social Cohesion
As co-living and co-working spaces bring together people from diverse cultural, professional, and socioeconomic backgrounds, they become microcosms of global society. The success of these environments depends on the ability to foster inclusion and mutual respect, particularly in cities with complex histories of migration, segregation, and inequality. Operators that invest in inclusive design, multilingual communication, and culturally sensitive programming can create spaces where residents and members feel seen and valued, regardless of origin or identity.
This dimension is especially relevant for WorldsDoor.com's exploration of culture and society. In co-living communities, shared meals, cultural festivals, and skill-sharing workshops can become platforms for cross-cultural understanding, while in co-working spaces, diverse teams collaborate on projects that span continents and disciplines. At the same time, there is a risk that globalized co-living brands impose a standardized aesthetic and lifestyle that erodes local traditions, especially in historic neighborhoods and smaller cities in Europe, Asia, and Latin America.
To navigate these tensions, some operators collaborate with local artists, cultural institutions, and community organizations, ensuring that their spaces reflect and support the surrounding culture rather than supplanting it. Others implement sliding-scale membership models or allocate space for local nonprofits and social enterprises, promoting socioeconomic diversity and community engagement. These practices align with broader movements toward inclusive urbanism and responsible tourism, themes that resonate strongly with readers interested in world affairs and ethical travel.
Strategic Implications for Businesses and Individuals
For businesses, the rise of co-living and co-working in 2026 demands a strategic reassessment of real estate, talent, and culture. Companies with globally distributed teams can leverage co-working networks to provide employees with professional environments near their homes, reducing the need for large central offices and enabling access to talent in secondary markets across North America, Europe, Asia, and Africa. Corporate partnerships with co-working providers allow for flexible scaling, project-based satellite offices, and localized innovation hubs closer to customers and partners.
At the same time, organizations must rethink how they cultivate culture and cohesion when employees work from a mix of home, co-working spaces, and occasional headquarters visits. Investment in digital collaboration tools, clear communication norms, and intentional in-person gatherings becomes essential. Leaders must also consider the wellbeing implications of highly flexible work arrangements, ensuring that employees have access to supportive environments, whether through stipends for co-working memberships or partnerships with co-living providers that meet high standards of health, safety, and ethics.
For individuals, co-living and co-working expand the menu of lifestyle choices. A young professional in London, a software engineer in Berlin, a designer in São Paulo, or a consultant in Singapore can choose from a spectrum of living and working configurations that balance stability and mobility, privacy and community, cost and experience. These choices are deeply personal, influenced by career goals, family obligations, cultural expectations, and health needs. As WorldsDoor.com continues to explore lifestyle, food, and wellbeing, it becomes clear that shared spaces are not just logistical solutions but also expressions of identity and aspiration.
Looking Ahead: Co-Creating the Next Generation of Shared Spaces
By 2026, co-living and co-working are firmly embedded in the global urban fabric, yet their future remains open and contested. Technological advances, climate imperatives, demographic shifts, and evolving social norms will continue to reshape how people share space. The most resilient and responsible models are likely to be those that combine strong financial foundations with genuine commitments to health, sustainability, cultural respect, and community empowerment.
For a globally oriented platform like WorldsDoor.com, the story of co-living and co-working is not merely about real estate or workplace trends; it is about how humanity navigates the complex transition to a more interconnected, urbanized, and digitally mediated world. Readers across the United States, United Kingdom, Germany, Canada, Australia, France, Italy, Spain, Netherlands, Switzerland, China, Sweden, Norway, Singapore, Denmark, South Korea, Japan, Thailand, Finland, South Africa, Brazil, Malaysia, New Zealand, and beyond are already participating in this transformation, whether by choosing flexible work arrangements, joining shared communities, or engaging in debates about the ethics and sustainability of these models.
As cities experiment with new regulations, as operators refine their offerings, and as residents and workers articulate their needs and boundaries, co-living and co-working will continue to evolve. The challenge and opportunity for all stakeholders is to ensure that this evolution advances not only efficiency and convenience but also human dignity, environmental responsibility, and cultural richness. In doing so, shared spaces can become not just places where people live and work, but platforms where healthier, more equitable, and more resilient societies are imagined and built, one community at a time.